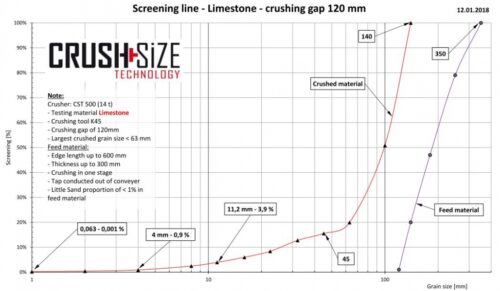
For the preparation of limestone to feed the rotary kiln or shaft kiln, it is necessary to achieve a specific grain band. In particular, the very low fines content and the negligible amount of oversize grain of the DRC crushers and the Sizers are of great importance for the energy-efficient treatment of limestone for the firing process in the rotary kiln or shaft furnace.
CRUSHING LIMESTONE, GYPSUM AND MARBLE
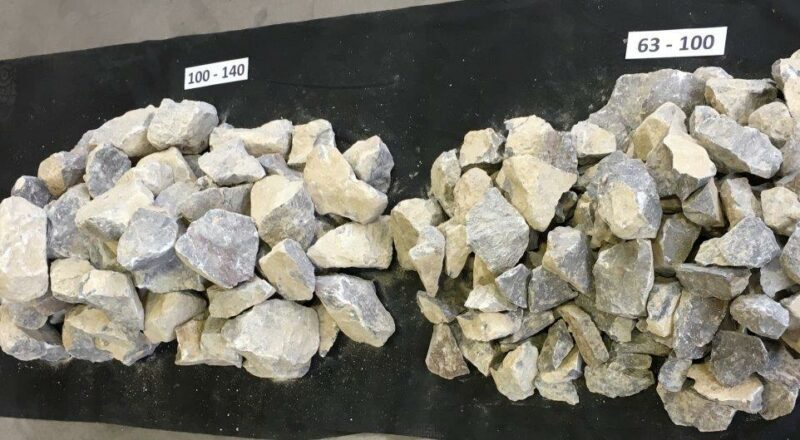
AS FEW LOSSES AS POSSIBLE
AS MUCH COARSE GRAIN AS POSSIBLE
The mechanical synchronization of the rollers ensures that the cubic grain shape is achieved. Synchronization positions the tools continuously with each other so that the geometric configuration produces a cubic grain shape. Likewise, an efficient feed of the material is achieved.
The hydraulically adjustable crushing gap ensures maximum process control. This allows the required grain sizes to be set efficiently and precisely.
CUBIC COARSE GRAIN
In particular, in the production of cement, where a coarse-grained limestone is needed in the shaft furnace or in the rotary kiln, the process property of coarse-grained crushing of the DRC series is of high importance.
What applies to the processing of limestone also applies in many cases to the processing of gypsum and marble.
RECOMMENDED MACHINE TYPES
The DRC series is particularly suitable for the efficient crushing of limestone, since the final grain size can be optimally adjusted thanks to the flexible crushing gap regulation. The DRC 900 can be used for primary crushing, where feed grain sizes of up to 1,200 mm are reduced to a final grain size of < 300 mm. In the secondary crushing stage, a DRC 700 is recommended in order to produce coarse-grained grain sizes of < 80 mm or < 120 mm, for example.
The Sizer (SZR) machine series is also equipped with mechanical synchronization of the roller rotation for efficient crushing. This means that it can also be used very effectively in primary and secondary crushing stages if you can do without the special properties of the DRC series (gap adjustment, overload protection).